Microsoft Certifications – Azure Solutions Architect Expert
[ How:to Learn & Earn this certification ]
Azure – New World of Development
Why get certified?
Certifications give you a professional edge by providing globally recognized industry endorsed evidence of skills mastery, demonstrating your abilities and willingness to embrace new technologies. Verify your skills—and unlock your opportunities.
Azure – Certification

What is the Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Expert Certification?
This complete certification consists of 2 certifications to complete: The two exam preparation must be required to earn the Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert Certification. You must complete the AZ-300 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies & AZ-301: Microsoft Azure Architect Design in order to become a Microsoft Certified Azure Solutions Architect Expert.
The AZ-300 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies certification tests and validates your expertise as an Azure Architect around Azure administration, Azure development, and DevOps; among a list of specific expertise categories within each of these.
The AZ-301 Microsoft Azure Architect Design certification tests and validates your expertise as an Azure Architect around Azure administration, Azure development, and DevOps; among a list of specific expertise categories within each of these.
Key Learning Areas for AZ-300 Certification
- How to manage their Azure resources, including deployment and configuration of virtual machines, virtual networks, storage accounts, and Azure AD that includes implementing and managing hybrid identities.
- Learn how cloud resources are managed in Azure through user and group accounts, and how to grant access to Azure AD users, groups, and services using Role-based access control (RBAC).
- Learn about the different storage accounts and services as well as basic data replication concepts and available replication schemes.
- Introduced to Storage Explorer as a convenient way to work with Azure storage data.
- Learn the types of storage and how to work with managed and custom disks.
- Azure blob storage is how Azure stores unstructured data in the cloud, and you will work with blobs and blob containers. In addition to blob storage, the course covers Table and Queue storage as storage options for structured data.
- Learn how to create and deploy virtual machines in Azure, using the Azure portal, PowerShell, and ARM templates. The course includes instruction on deploying custom images and Linux virtual machines. You will see how to configure the networking and storage components of virtual machines. Deploying highly available virtual machines is critical for planned and unplanned events, and you will learn how to use availability sets to ensure that virtual machine resources are available during downtime.
- You will dive into the cloud design patterns that are important, such as partitioning workloads where a modular application is divided into functional units that can be integrated into a larger application. In such cases, each module handles a portion of the application’s overall functionality and represents a set of related concerns.
- Load balancing where the application traffic, or load, is distributed among various endpoints by using algorithms. Load balancers allow multiple instances of your website to be created so they can behave in a predictable manner. In Azure, it is possible to use virtual load balancers, which are hosted in virtual machines, if a company requires a very specific load balancer configuration.
- Transient fault handling which helps define the primary differences between developing applications on-premises and in the to handle transient errors. Transient errors are errors that occur due to temporary interruptions in the service or to excess latency.
- Discussion of hybrid networking that provides an overview of site-to-site connectivity, point-to-site connectivity, and the combination of the two.
- To build Logic App solutions that integrate apps, data, systems, and services across enterprises or organizations by automating tasks and business processes as workflows. Logic Apps is cloud service in Azure that simplifies how you design and create scalable solutions for app integration, data integration, system integration, enterprise application integration (EAI), and business-to-business (B2B) communication, whether in the cloud, on-premises, or both.
- How Azure Service Fabric is a distributed systems platform that makes it easy to package, deploy, and manage scalable and reliable microservices and containers. Service Fabric also addresses the significant challenges in developing and managing cloud-native applications. Developers and administrators can avoid complex infrastructure problems and focus on implementing mission-critical, demanding workloads that are scalable, reliable, and manageable. Service Fabric represents the next-generation platform for building and managing these enterprise-class, tier-1, cloud-scale applications running in containers.
- See how Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) makes it simple to deploy a managed Kubernetes cluster in Azure. AKS reduces the complexity and operational overhead of managing Kubernetes by offloading much of that responsibility to Azure. As a hosted Kubernetes service, Azure handles critical tasks like health monitoring and maintenance for you.
- Learn how to Implement authentication in applications (certificates, Azure AD, Azure AD Connect, token-based), implement secure data (SSL and TLS), and manage cryptographic keys in Azure Key Vault.
- Learn how to configure a message-based integration architecture, develop for asynchronous processing, create apps for autoscaling, and better understand Azure Cognitive Services solutions.
Links to Instructor-Led Training
- AZ-300T01: Deploying and Configuring Infrastructure
- AZ-300T02: Implementing Workloads and Security
- AZ-300T03: Understanding Cloud Architect Technology Solutions
- AZ-300T04: Creating and Deploying Apps
- AZ-300T05: Implementing Authentication and Secure Data
- AZ-300T06: Developing for the Cloud
PointGuide – Create an event hub using the Azure portal
Azure Event Hubs is a Big Data streaming platform and event ingestion service, capable of receiving and processing millions of events per second. Event Hubs can process and store events, data, or telemetry produced by distributed software and devices. Data sent to an event hub can be transformed and stored using any real-time analytics provider or batching/storage adapters. For a detailed overview of Event Hubs, see Event Hubs overview and Event Hubs features.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, make sure that you have:
- Azure subscription. If you don’t have one, create a free account before you begin.
- Visual Studio 2017 Update 3 (version 15.3, 26730.01) or later.
- .NET Standard SDK, version 2.0 or later.
- Resource Group on Azure
- Event Hubs namespace on Azure
Create an event hub
To create an event hub within the namespace, do the following actions:
- On the Event Hubs Namespaces page, select click Event Hubs
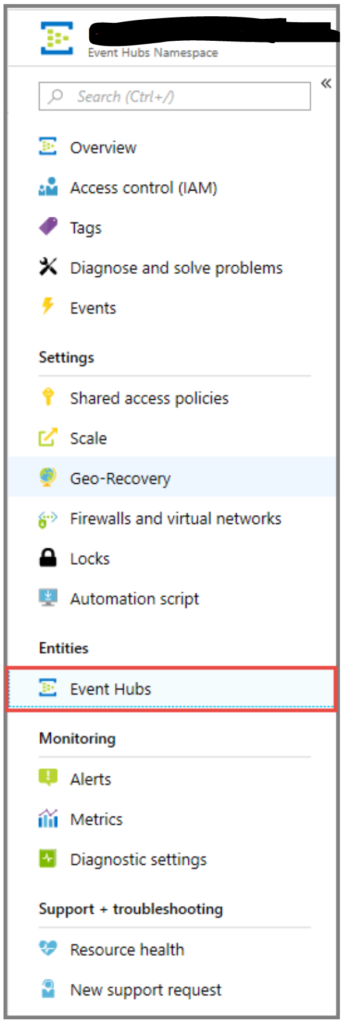
- At the top of the window, click + Event Hub.
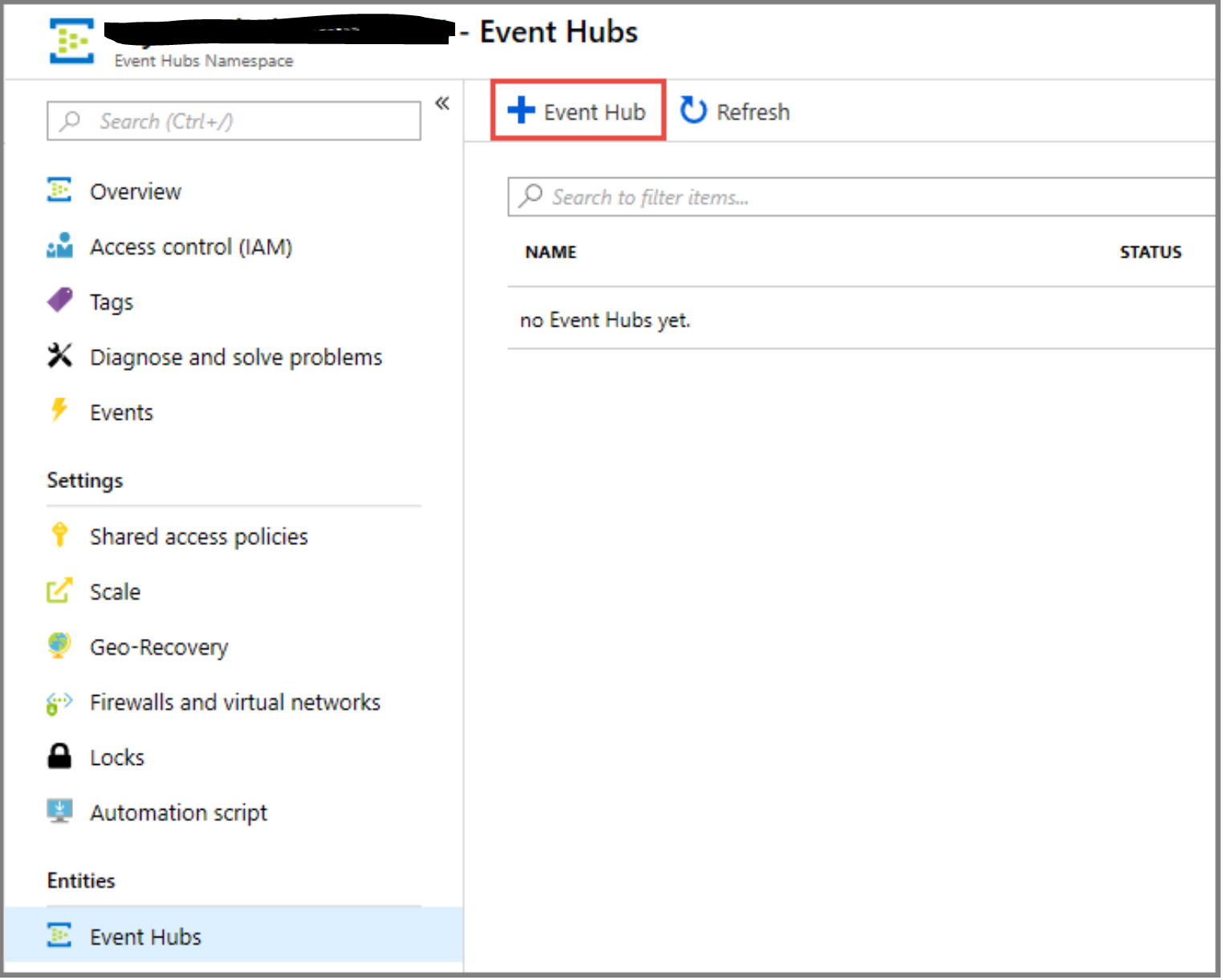
- Type a name for your event hub, then click Create.
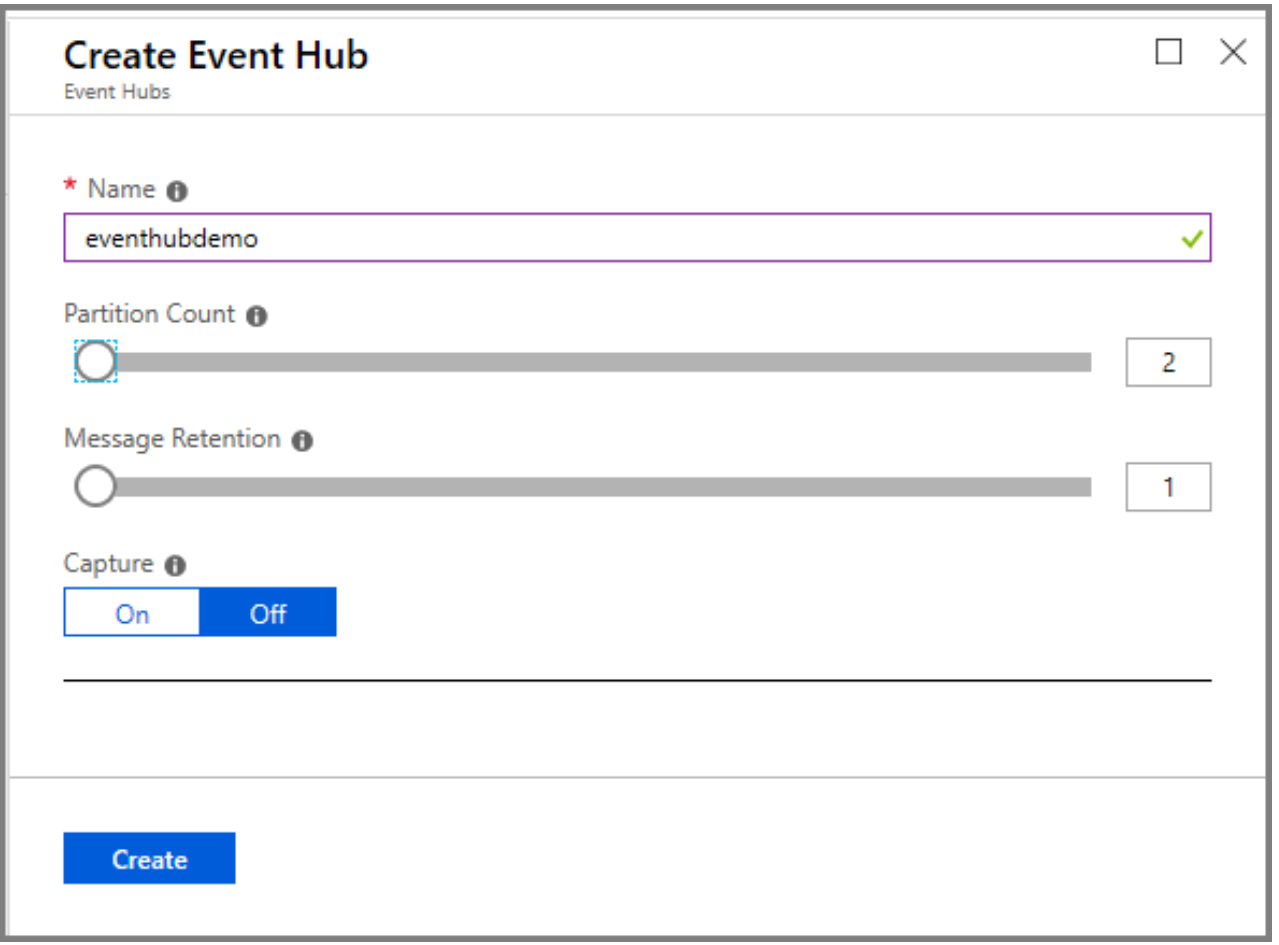
Congratulations! You have used the portal to create an event hub within a Event Hubs namespace.