Azure Digital Machines – Superior
- Configuring the Availability Set of your Digital Machine, as a way to increase the provision as much as 99.99% uptime assured by SLA;
- Executing PowerShell script into your Digital Machine, by way of the Run Command;
- Easy methods to migrate current VHDs, to run on Azure Digital Machines;
With a purpose to perceive higher this text, please verify my earlier article explaining the fundamentals of Azure Digital Machines,
To benefit from Azure 99,99% uptime assured SLA you will need to take some steps as follows,
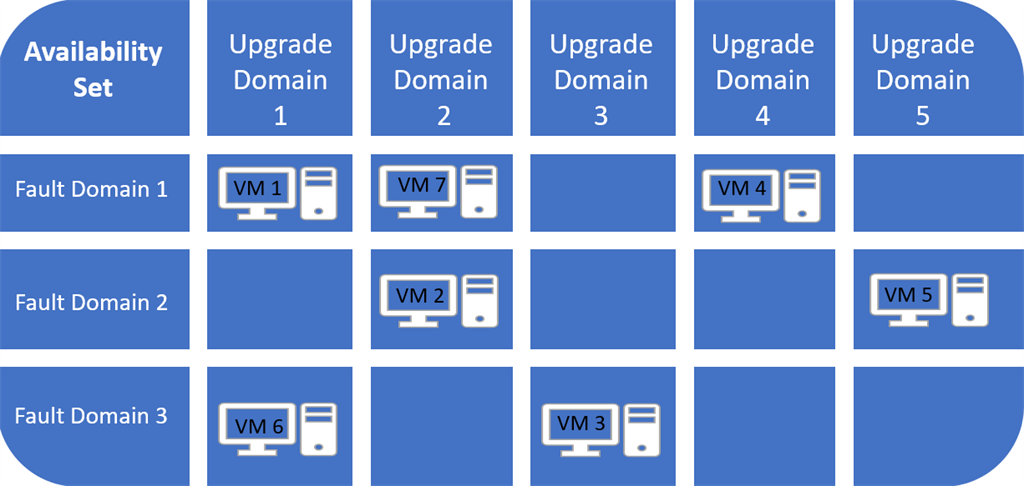
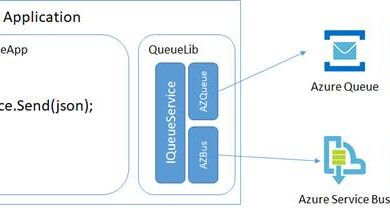
Availability units
Availability units can defend you from:
- System Reboots, to use updates;
- {Hardware} failures;
- Community issues;
- Lack of vitality.
However… how?
One availability set accommodates a set of replace domains and fault domains that run in the identical datacenter.
Replace domains are the place redundancy is utilized to keep away from a system reboot to impression all of your Digital Machines, in the identical replace area group, as a result of updates within the Azure platform.
Fault domains are the place redundancy is utilized to keep away from faults({hardware}, vitality or community issues) on {hardware} or software program to impression all of your Digital Machines operating in the identical fault area group.
When deploying Digital Machines right into a single Availability Set, the Availability Set goes to distribute your VMs mechanically among the many Fault & Replace Domains as follows:
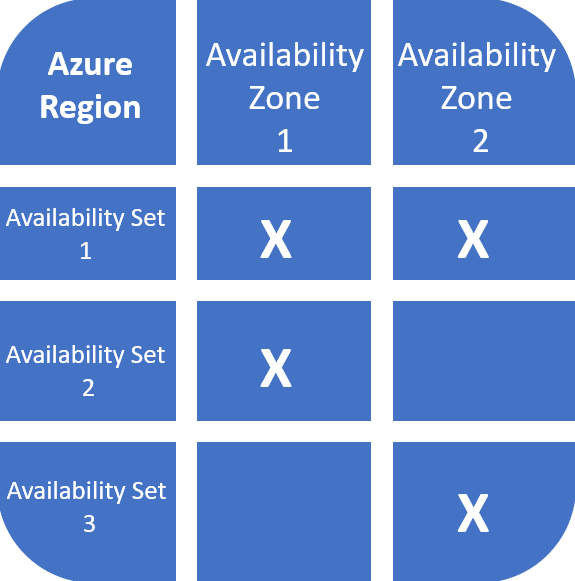
Availability Zones
Availability Zones are Availability Units operating in several datacenter areas in the identical Azure Area. It implies that they’re bodily separated inside one another, stopping knowledge middle failures and elevating the assured uptime SLA to 99.99%.`
Azure managed disks
Azure Managed Disks are bodily disks however virtualized. It brings a number of advantages to your Digital Machine as follows:
- Extremely accessible, is designed to have 99,999% uptime having three replicas of your knowledge;
- Extremely sturdy, having a 0% failure price;
- Built-in with Availability Units, to keep away from single level failure;
- Scalability, having the ability to deploy as much as 1.000 VMs per scale set;
- Azure Backup, managing and scheduling your backups;
- Direct add, being simpler to deal with your disk knowledge.
Handle OS Upgrades with scheduled occasions
With Scheduled Occasions, chances are you’ll plan for Digital Machine upkeep as a way to keep away from any impression in your shoppers and providers so far as your Digital Machine might want to go down for some time.
Metadata Service API
- If in case you have VNet in your Digital Machine enabled, that is the endpoint at at this time’s date,
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2019-01-01 - For Digital Machines with out VNet enabled, you will need to comply with this tutorial to find your endpoint,
https://github.com/azure-samples/virtual-machines-python-scheduled-events-discover-endpoint-for-non-vnet-vm
Samples for Querying the API
You have to make these calls out of your Digital Machine PowerShell
Request for Occasions:
- $metadataEndpoint = ‘http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2019-01-01’
- Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{“Metadata”=“true”} -URI $metadataEndpoint -Technique get
- $metadataEndpoint = ‘http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2019-01-01’
- Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $metadataEndpoint -Headers @{“Metadata”=“true”} -Technique POST -Physique ‘{“StartRequests”: [{“EventId”: “<your event id goes here>”}]}’
Enabling and disabling Scheduled Occasions
- Enabled mechanically after making a request to the Metadata Service API;
- Disabled mechanically after not making any request to the Metadata Service API for 24 hours.
P.S: Scheduled occasions aren’t accessible in each Azure Area, verify area availability:
Utilizing a Load Balancer to distribute incoming calls
The Load Balancer is a good software to distribute your incoming request by way of your Digital Machines as a way to don’t overload any Digital Machine, distributing requests amongst your accessible Digital Machines in accordance with your wants.
Well being Probe
Well being probes are going to always run a well being verify, based mostly on configurations set by you, in opposition to your VMs as a way to set your VMs to be accessible or unavailable to obtain requests.
Load Balancer Guidelines
We create guidelines within the Load Balancer to outline how the incoming site visitors move goes to be distributed among the many accessible Digital Machines. You may additionally configure if you’d like a Well being Probe operating together with your rule as a way to don’t distribute incoming site visitors to your unhealthy VMs.
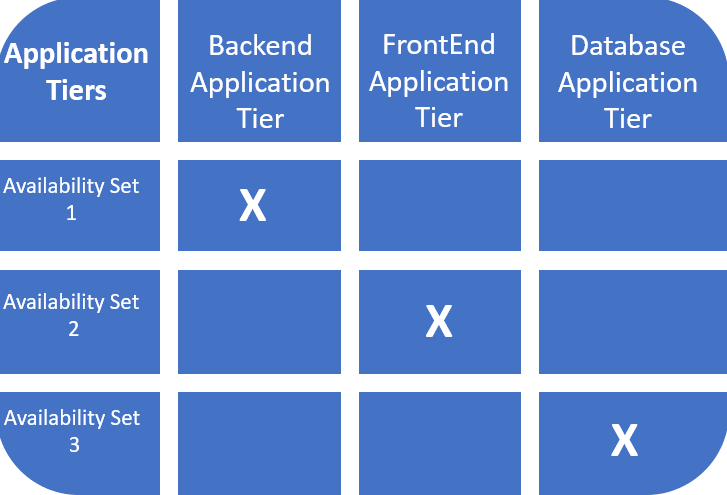
Utility Tiers
Purposes that make utilization of their software program structure being grouped in tiers might benefit from Utility Tiers, as a way to group your tiers in a special group of Digital Machines. So that you’re capable of separate your software tiers in several availability zones or availability units.
A great observe can be to have every tier of your software in a special Utility Tier and having every Utility Tier in a special Availability Set/Zone. Remembering that an Availability Set/Zone works higher with a number of Digital Machines.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/home windows/manage-availability
Working PowerShell scripts in your Azure Home windows VM
Chances are you’ll use the Run Command characteristic to run PowerShell instructions remotely by your VM Agent in your Digital Machine. It presents a quick and secure approach to run instructions in your Digital Machine as a way to diagnose, troubleshoot and remediate points which can be affecting your VM.
Out there instructions to run by way of the run command:
- RunPowerShellScript, the place chances are you’ll run your customized script;
- EnableRemotePS, enabling your VM to simply accept distant PowerShell instructions;
- EnableAdminAccount, enabling admin account;
- IPConfig, working as regular IPConfig command;
- RDPSettings, exhibiting registry and area coverage settings;
- ResetRDPCert, eradicating SSL certificates and resetting your RDP listener;
- SetRDPPort, setting the port quantity for Distant Desktop Entry.
Working scripts remotely has some limitations, as Microsoft describes:
- Script Output is restricted to the final 4,096 bytes.
- The minimal time to run a script is about 20 seconds.
- Scripts run as System on Home windows.
- One script at a time can run.
- Scripts that immediate for info (interactive mode) aren’t supported.
- You’ll be able to’t cancel a operating script.
- The utmost time a script can run is 90 minutes. After that, it’ll trip.
- Outbound connectivity from the VM is required to return the outcomes of the script.
Migrating current VHDs to Azure VM
If in case you have an current VHD and desires emigrate to Azure Digital Machine you possibly can migrate it with none downside utilizing PowerShell, as follows:
Variables used round code,
- $diskName= “sampleDisk”
- $diskLocalPath=“C:myFolderdisk.vhd”
- $imageName=“sampleImage”
- $location= “yourLocation”
- $resourceGroup= “sampleResourceGroup”
- $virtualMachineName=“sampleVm”
Add your VHD,
- #grants a short-term write entry
- $diskTempAccess = Grant-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -DiskName $diskName -DurationInSecond 86400 -Entry ‘Write’
- #copy your disk
- AzCopy.exe copy $diskLocalPath $diskTempAccess.AccessSAS –blob-type PageBlob
Create an Picture out of your VHD,
- $disk = Get-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -DiskName $diskName
- $imageConfig = New-AzImageConfig
- -Location $location
- $imageConfig = Set-AzImageOsDisk
- -Picture $imageConfig
- -OsState Generalized
- -OsType Home windows
- -ManagedDiskId $disk.Id
- $picture = New-AzImage
- -ImageName $imageName
- -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup
- -Picture $imageConfig
Create a brand new Digital Machine utilizing the copy of your VHD,
- New-AzVm `
- -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup
- -Identify $virtualMachineName
- -Picture $picture.Id
- -Location $location
- -VirtualNetworkName “your Vnet”
- -SubnetName “your subnet”
- -SecurityGroupName “your safety group”
- -PublicIpAddressName “your ip”
- -OpenPorts 3389
Full code
- $diskName= “sampleDisk”
- $diskLocalPath=“C:myFolderdisk.vhd”
- $imageName=“sampleImage”
- $location= “yourLocation”
- $resourceGroup= “sampleResourceGroup”
- $virtualMachineName=“sampleVm”
- #add ——————————————————
- #grants a short-term write entry
- $diskTempAccess = Grant-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -DiskName $diskName -DurationInSecond 86400 -Entry ‘Write’
- #copy your disk
- AzCopy.exe copy $diskLocalPath $diskTempAccess.AccessSAS –blob-type PageBlob
- #create customized picture —————————————–
- $disk = Get-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -DiskName $diskName
- $imageConfig = New-AzImageConfig
- -Location $location
- $imageConfig = Set-AzImageOsDisk
- -Picture $imageConfig
- -OsState Generalized
- -OsType Home windows
- -ManagedDiskId $disk.Id
- $picture = New-AzImage
- -ImageName $imageName
- -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup
- -Picture $imageConfig
- #create VM
- New-AzVm `
- -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup
- -Identify $virtualMachineName
- -Picture $picture.Id
- -Location $location
- -VirtualNetworkName “your Vnet”
- -SubnetName “your subnet”
- -SecurityGroupName “your safety group”
- -PublicIpAddressName “your ip”
- -OpenPorts 3389
Exterior References